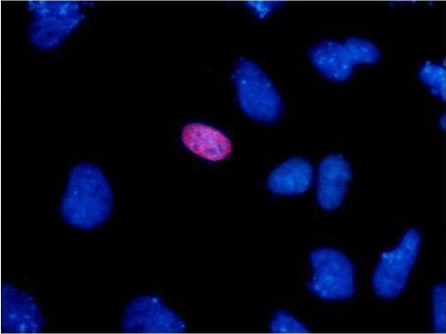
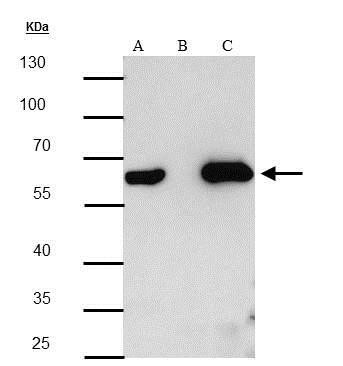
The HA tag is derived from an epitope of the influenza hemagglutinin protein which has been used extensively as a general epitope tag in expression vectors.
Human influenza hemagglutinin (HA) is a surface glycoprotein required for the infectivity of the human virus. The HA tag is derived from the HA molecule corresponding to amino acids 98-106 has been extensively used as a general epitope tag in expression vectors. Many recombinant proteins have been engineered to express the HA tag, which does not appear to interfere with the bioactivity or the biodistribution of the recombinant protein. This tag facilitates the detection, isolation, and purification of the proteins.
Human influenza hemagglutinin (HA) is a surface glycoprotein required for the infectivity of the human virus. The HA tag is derived from the HA molecule corresponding to amino acids 98-106 has been extensively used as a general epitope tag in expression vectors. Many recombinant proteins have been engineered to express the HA tag, which does not appear to interfere with the bioactivity or the biodistribution of the recombinant protein. This tag facilitates the detection, isolation, and purification of the proteins.